ERC4337 is an Ethereum standard that achieves account abstraction on the protocol without any consensus-layer changes. Deployed on the Ethereum mainnet in March 2023, ERC4337 makes it possible to transact and create contracts in a single contract account.
Account abstraction opens the door to user-friendly crypto wallet designs that could potentially facilitate broader adoption.
How ERC4337 Works
The Ethereum protocol uses an account-based model, ERC4337 combines features of the protocol’s two existing account types:
- Externally Owned Accounts (EOA) – are owned and controlled by users (like your Metamask wallet account)
- Smart contract accounts – are associated with bytecode stored on the network.
The result is a single contract account making innovative smart contract based wallet designs possible.
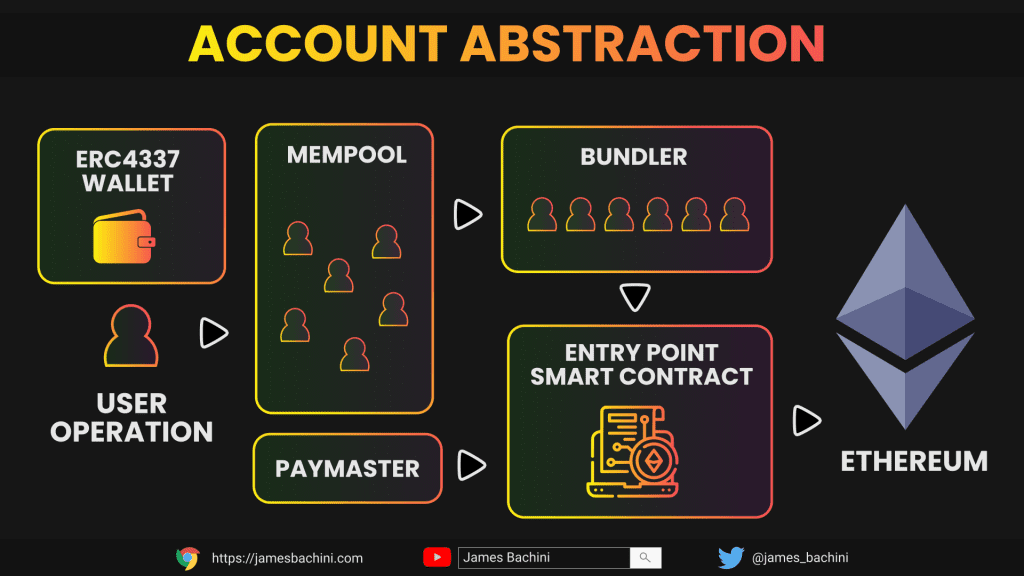
ERC4337 introduces a new object called a UserOperation. Different users send UserOperation transactions into an alternative 3rd party mempool where bundlers package these into a bundled transaction and execute a single on-chain transaction.
A paymaster will pay gas for the bundled transactions and either sponsor the gasless transaction or get paid fees by the individual UserOperation executions.
Account Abstraction Use Cases
Account abstraction offers a number of potential benefits for users and the Ethereum protocol.
Network Scalability
EIP 4337 improves the scalability of the Ethereum network by introducing bundled transactions, which allow multiple userOperation’s to be executed within a single network transaction.
This combined with the sharding update and the migration to layer 2 rollups means that data and blockspace is going to become cheaper, faster and more efficient.
Gasless Transactions
Users can potentially pay for transaction costs in non-ETH tokens like stablecoins. The block producer will then automatically swap the tokens for ETH to cover the gas cost behind the scenes, making it easier and more convenient to use.
There is also the potential for paymasters to sponsor transactions based on a subscription model or even as an incentive to use a particular blockchain.
UX & Security
EIP 4337 introduces programmable wallets making things like multi-signature wallets with social recovery features that make signing in, password authentication, and account recovery easier. This has the potential to improve security systems that we use to self-custody assets and make it more accessible for non-technical users.
Building Bundlers
There is a reference bundler built by the original authors of EIP4337 here: https://github.com/eth-infinitism/bundler
You can run this locally with:
yarn && yarn preprocess
yarn hardhat-deploy --network localhost
yarn run bundlerThis will fire up a local node on port 3000 which allows us to execute userOps
yarn run runop --deployFactory --network http://localhost:3000/ --entryPoint 0x0576a174d229e3cfa37253523e645a78a0c91b57This operation deploys a wallet deployer, creates a random signer, determines the wallet address, adds funds, sends a TX to create the wallet and another from this new wallet.
Conclusion
ERC4337 aims to achieve account abstraction through enabling innovative use cases to ultimately improve the user experience and increase the networks scalability.
Critics of ERC4337 may argue that it will make Ethereum wallets more complex, potentially introducing new bugs, attack vectors, and centralization around the bundlers.
Ethereum needs to scale and bundling transactions will play an important part in the multi pronged scaling infrastructure we see rolling out over the coming years. This will make working with blockchains more capable and less technical, with much of the complexity hidden behind the scenes.
We need account abstraction and smart wallets for the blockchain sector to reach mainstream adoption.


