This article will explore how prompt engineering for LLM models like ChatGPT is evolving and how you can stay ahead of the game.
- Prompt Design Principles
- 5 Example Prompt Templates
- Multimodal Prompting Beyond Text
- AI Prompt Generation
- The Future Of Prompt Engineering
Prompt Design Principles
As large language models (LLMs) continue to evolve, the art of prompt engineering has become increasingly crucial. At its core, effective prompt design hinges on clarity, specificity, and context (CSC).
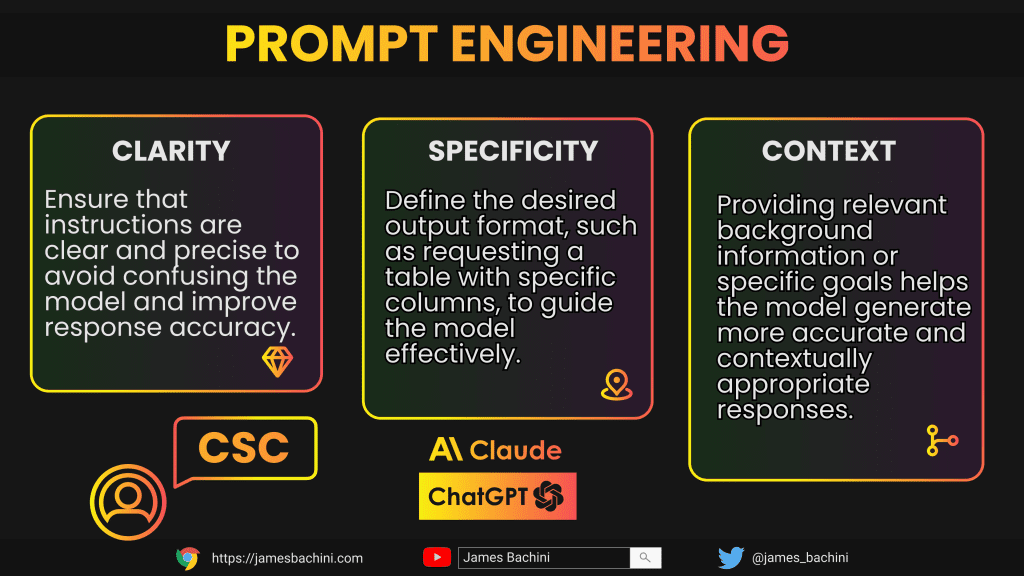
A well crafted prompt should unambiguously convey the desired task or information, providing sufficient context without overwhelming the model.
One key principle is to break complex queries into smaller, manageable steps. This approach, often referred to as chain of thought prompting, allows the model to tackle intricate problems systematically. Another aspect is the inclusion of relevant examples within the prompt, which can significantly enhance the model’s understanding and output quality.
It’s also essential to consider the model’s limitations and biases. Prompts should be designed to mitigate potential biases and to work within the constraints of the model’s training data and capabilities.
Designing effective prompts is both an art and a science. The main goal is to communicate your intent clearly so that the model can provide accurate and relevant results. Key principles include:
- Clarity
Ambiguous instructions can confuse the model. Prompt engineers must ensure that each instruction is clear and unambiguous. For example, instead of “Explain renewable energy,” specify the type of energy and its impact, such as “Describe the environmental benefits of solar energy.” - Specificity
Explicitly defining the expected output format enhances the likelihood of receiving a useful response. If the model should generate a table, structure the prompt to include, “Present the data in a table format with three columns: item, quantity, and cost.” - Context
Models perform better when they are given appropriate context. Providing situational background or explaining the task’s goal is key. For instance, instead of “Translate the text,” use “Translate this legal contract from Spanish to English, ensuring legal terminologies are accurately conveyed.”
5 Example Prompt Templates
These templates serve as starting points and can be adapted to suit various needs and contexts.
Task Oriented Template
"As a [role], your task is to [specific action]. Consider [relevant factors] and provide [expected output format]."Comparative Analysis Template
"Compare and contrast [subject A] and [subject B] in terms of [specific aspects]. Highlight key similarities and differences, and conclude with your assessment of [relevant criterion]."Step-by-Step Guide Template
"Create a detailed guide on how to [accomplish task]. Begin with [starting point] and end with [desired outcome]. Include any necessary precautions or tips."Problem Solving Template
"You are faced with [problem scenario]. Analyse the situation, identify potential solutions, and recommend the best course of action. Explain your reasoning."Data Extraction Template
"Extract and list all company names and people's names mentioned in the following text: [Insert text here]. Format as a csv
CompanyName,PeoplesName"Multimodal Prompting Beyond Text
As AI models advance, prompting is no longer limited to text inputs. Multimodal prompting incorporates various data types, including images, audio, and video. This approach opens up new possibilities for interaction and problem-solving.
For instance, in image > text models, a prompt might include both a textual description and an image, allowing for more nuanced and context-rich interactions. Similarly, audio > visual prompts can be used for tasks ranging from content creation to complex analysis in fields like medicine or engineering.
The key to effective multimodal prompting lies in understanding how different modalities complement each other and how to leverage their combined strengths to achieve the desired outcome.
AI Prompt Generation
An intriguing development in the field is the use of AI to generate prompts. We’ve seen this already with the latest ChatGPT models and Anthropic has talked about having specialist models to do different tasks and then a manager model to assign roles.
The potential benefits are significant, including increased efficiency, discovery of novel prompting strategies, and the ability to tailor prompts to specific models or tasks automatically.
Today we can ask LLM’s for tips on how to improve our prompts. The outputs require testing but it’s a useful way to align and ensure you are providing all the required information.
AI generated prompts can be particularly useful in optimising for specific outcomes or in navigating the complexities of advanced language models. However, this approach also raises questions about the role of human creativity and intuition in the prompting process.
The Future Of Prompt Engineering
Looking ahead, prompt engineering is poised to become an even more critical skill. As models become more sophisticated, the ability to effectively communicate with and guide these AI systems will become extremely valuable.
We can anticipate the development of more standardised prompting languages, akin to programming languages, designed specifically for interaction with AI models. These languages could offer more precise control over model outputs and behaviours.
As AI continues to permeate various sectors, prompt engineering skills will likely become essential across diverse professions, from data science to creative industries. The future may see the emergence of specialised prompt engineers who bridge the gap between human intent and AI capabilities.
While AI is destined to become better at understanding our requirements it is still going to be our job to communicate them effectively.