This article is part of a free online course where you can learn digital marketing.
In this article we are going to go through the complete process of creating SEO content that ranks at the top of Google.
- SEO in 90 Seconds
- What Content Ranks Well On Google
- Keyword Research
- High Click Through Rate Titles
- Title Suggestion Tool
- SEO Content Structure
- Snippet Optimization
- OnPage Optimization
- Copywriting & Editing
- Link Building, Outreach & Seed Marketing
- 7 SEO Content Tips
SEO in 90 Seconds

What Content Ranks Well On Google
There is a paradox in creating content that ranks well with the search engines. On one hand we need to write content that exceeds visitors expectations. Content that real people want to consume, share and link to. On the other hand we need to write content that meets with the search engine algorithm’s requirements.
A strong content strategy needs to please both the website visitors and the search engine spiders.
Visitors want quality content, search engines want quantity
This may change in the future but the more content you create around a topic the more likely it is to rank well in the search engines.
From our internal analysis the average article ranking for competitive terms is 1874 words long and is just under 3 years old. Google’s search engine ranks mature long-form content higher.
One reason that mature (often updated) articles do well is that they have had time to build up a strong backlink and social indicator profile.
There are 7 forms of content that I would recommend incorporating in a content strategy.
- The Long Form Blog Post
- Original Research
- Lengthy Lists
- How To Guides
- Content Hubs
- Perpetual Annual Reviews
- SEO Video Content
The Long Form Blog Post

The long form blog post is usually between 1000 and 8000 words. It’s a comprehensive answer to a targeted query.
This forms the staple of many SEO bloggers content production. The final word count required depends a lot on the competition currently in the SERP’s (search engine results pages).
| Competition | Post Type | Notes | Content Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lowest | Response Post | A concise post with condensed value. | 1000 words |
| Low | Standard Post | Bread and butter post, quality media, well laid out, linkbait & strong content | 2000 words |
| Medium | Pillar Post | Best possible content, an eBook in a blog post | 3000+ words |
Signs of high competition:-
- Is the top result a direct answer to the query?
- Is the top result a high authority domain in the results?
- Is there a wikipedia/.gov result in the results?
- Is there a relevant long form blog post in the search results?
- Is there a well formatted snippet at the top of the results?
Signs of low competition:-
- Is the top result an unknown site you haven’t heard of previously?
- Does the top result have good media?
- Does the top result have a good layout? Contents, sub-heading
- Is the top result inundated with ads?
- Is a Quora/Forum post in the search results?
- Is there posts that are 2+ years old in the results?
When creating long form articles it can be difficult to keep the quality high so that visitors will actually want to read it all or at least scan it all.
The best way to do it is to create a contents section first. This is a group of headings which breaks down a topic into sub-topics or sections.
If you know you need 2000 words and each sub-topic you can comfortably write 200 words without filler then you need 10 core sub-topics.
Once the contents are laid out it’s much easier to write out useful high quality content for each sub-topic.
Original Research

Original research is the ultimate link magnet. High quality publications look for research and statistics to back up their own content.
If you can analyse some data, collect a survey or draw up some charts then do it.
99% of the competition either can’t or aren’t motivated to do original research. Most content is regurgitated from one blog post to the next and anything new will stand out and build authority in the niche.
Here are some ideas for original research:-
- Industry Survey – Can use google forms to collect data from industry players
- Data Visualisation – Tools like tableau can present data in new ways
- Site Scraping – Create a simple spider to collect data from industry websites
- Social Media Analysis – What industry insights can be drawn from social media API’s
- Data Collection – Collecting data such as pricing over a longer period of time
- Theorise – Propose a new theory
- Tests – Create a hypothesis, test it and show the results
- What I learned From x – In the trenches documenting a journey or challenge
Lengthy Lists

Lists go viral for a reason and there’s something about numbers in a title that make it more clickable. It’s structured content that sets expectations and visitors love it. Expand this to long-form content for the algorithms and we have a winning combination.
A lengthy list should have as many items as possible. It’s not unusual to see lists of 100+ items doing well in the SERP’s.
This brings shock and awe to the title:
“158 Tools For Internet Marketing”
“172 Spam Indicators Preventing Email Delivery”
There’s no way a potential visitor knows about all of them so they are guaranteed to learn something.
Lengthy lists also work well as a form of linkbait. If the list is definitive and the content is good and useful then it will get shared and linked to.
Some tips for writing lengthy lists:-
- Start of by researching the list items
- Break the list into categories such as “SEO Tools”, “Blogging Tools”, “Facebook Tools”
- Find as many as possible, aim for 100
- Don’t worry about finishing on a round number
- Once the list is compiled go through and write some content for each item
- Include media such as screenshots or images
- Link out to the resources if possible (open in new window)
- Use headings and make the list scannable
- Create a contents section near the start of the article with a link to each item broken down by category.
How To Guides

A how to guide or step by step guide is education content. It should inform the user and provide actionable content. The target keyword should be something that is specifically searched for and want to learn about.
Start by outlining the process in the form of steps. These can form the contents and sub-headings for the article.
Include lots of images and screenshots to make the post visually appealing.
Content Hubs

A content hub acts as a gateway page to additional sub-topics on a subject. It can be laid out as an online course or resource center. Each sub-topic will have an individual post which will link back to the content hub page via breadcrumbs navigation.
A content hub should have at least 10 sub-topic posts. Each sub-topic may follow a similar format such as:-
- What is X
- Why X is Important
- Actionable Advice
- Future reading internal/external links
This is one of the most powerful strategies to rank for competitive terms right now. It takes a lot of work to build so should only be used for relatively high volume keywords.
Content hubs provide an outstanding user experience and get linked to a lot naturally. It is also an ideal platform to launch an outreach campaign telling peers about the new resource.
Perpetual Annual Reviews

Annual type posts such as “2020 Niche Predictions” and “Best of Niche 2020” tend to get high click through rates and get shared a lot.
The key thing with this type of content is to make it evergreen by using a custom URL or permalink.
If we use the “2020 Niche Predictions” title for example, WordPress will automatically format the URL to https://example.com/2020-niche-predictions/
We want to change this using the document settings to:
https://example.com/niche-predictions/
This will allow us to revisit the post annually and update it with the latest predictions. The benefit of this is that it will already have a backlink and social signal profile from previous years making it easier to rank and get high click through rates.
SEO Video Content

Video content from Youtube is showing up at the top of the SERP’s for more and more terms. Google owns Youtube and sells advertising on the site, therefore having a vested interest in promoting this content.
By including an embedded Youtube video in your post you get two opportunities to rank. In the traditional SERP’s and in the Youtube video results. While the traffic from this is going to Youtube rather than your own site it can still be an effective way to build a brand and gain an audience for competitive terms.
Keyword research is key and Youtube’s search algorithm is similar but not identical to Google’s main search. In addition there is additional data available, most notably:-
- Number of views per video in the results
- Number of subscribers each creator has that is ranking
- Transparent engagement stats such as likes, comments
This will give us insights into how hard it will be to get our own content into these results.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the difference between having a popular website and having a blog that you use to vent and no one reads.
The main idea is to find out what people are searching for regularly in the niche. Then figure out how much search volume there is and how hard it will be to rank our own content for that keyword phrase.

There are a number of tools that automate this process and provide in-depth analysis of the keywords. However in competitive niches it’s common that everyone has access to these tools and you see a lot of competition for the same terms that these tools report as being “good”.
The optimum method is to develop a custom process to come up with keyword ideas that no one else is using.
How To Find Out What People Are Searching For
The first step is to find out what people are searching for and there are many ways we can go about building out a keyword list.
- Brainstorming – what do you search for in this niche regularly and expand ideas around that. Open up a text editor and rapidly write out all the common search phrases you can think of. This is a manual, labour intensive process but one that guarantees original results.
- Auto-suggest – type the first part of a search query into google and an auto-suggest box will pop up offering commonly searched terms. I like this method so much I built a custom automated script to explore niche ideas.
- Related Searches – If you google a niche keyword then you in the results you’ll often see suggestion boxes such as “People also asked” and “Searches related to …”. These can provide insights into what terms Google’s algorithm most closely matches.
- Google Ads Keyword Planner – Add seed phrases to the discover new keywords tool to get a list of related terms.
- Question Sites – Sites such as QuestionDB, AlsoAsked and AnswerThePublic can provide a quick exploratory method to discover related terms and questions that consumers are searching.
A combination of all of these methods can be used to explore a niche and build a really big list of keyword phrases for the next step. Doing this manually can help fine tune the method which can be automated or semi-automated later.
Analysing Search Traffic Volumes
We then take this big list and put it into Google ads keyword planner to get the monthly search volumes. Make sure that the country is accurate to your target region in the settings at the top. Order the results by impressions with highest first and then download the .csv file or open it up in Google Sheets.
Remove any results that don’t get any traffic. We now have a custom niche specific list of keyword phrases with the search volumes.
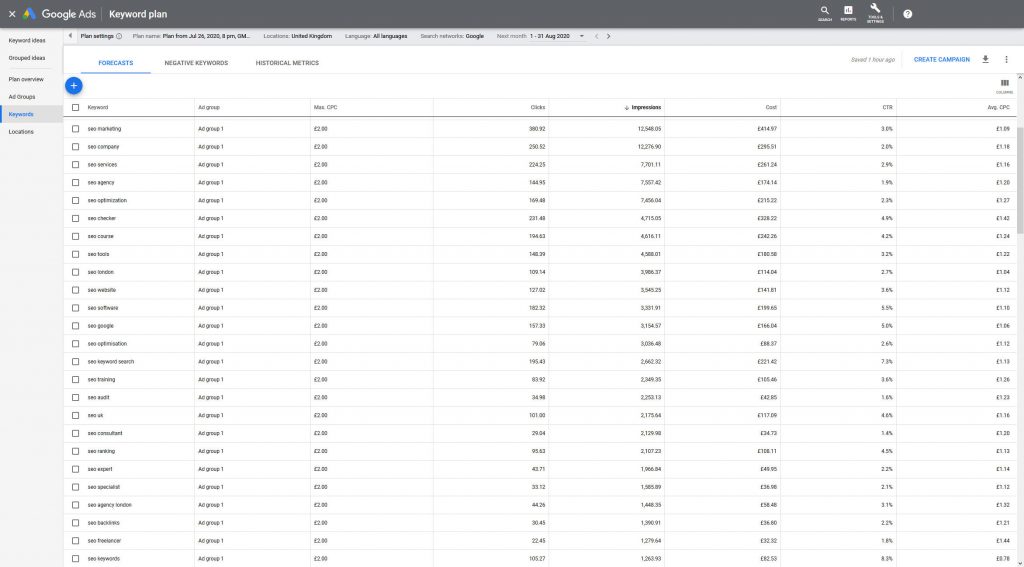
Assessing Ranking Difficulty
Some keywords are just not worth fighting for. Be realistic and don’t develop content that is never going to rank for the target keywords which have also been targeted by high authority household name websites.
There’s automated tools that will give a basic analysis of the search difficulty for each keyword and these can be useful for filtering a big list. Once you have it down to 10-20 potential topics it’s a good idea to go through each one individually and look at the current search results pages.
Signs of high competition:-
- Is the top result a direct answer to the query?
- Is the top result a high authority domain in the results?
- Is there a wikipedia/.gov result in the results?
- Is there a relevant long form blog post in the search results?
- Is there a well formatted snippet at the top of the results?
Signs of low competition:-
- Is the top result an unknown site you haven’t heard of previously?
- Does the top result have good media?
- Does the top result have a good layout? Contents, sub-heading
- Is the top result inundated with ads?
- Is a Quora/Forum post in the search results?
- Are there posts that are 5+ years old in the results?
Each keyword term can be given an assessment score. This can be considered alongside the search volumes and keyword term itself to decide which keywords provide the most search traffic while being possible to rank for.
Keyword Tips
- Not all keywords are created equally and often low competition, high volume keywords have little buyer intent.
- Consider search intent when doing analysis. Sometimes Google shows results for semantically matched keyword phrases which affects search volume and difficulty stats when using automated tools.
- At a minimum there needs to be an opportunity to rank on the first page. If the top result is hard to beat but everything underneath is relatively low quality then target the featured snippet to jump ahead.
- Keep the lists of keywords as they can come in handy later. When building content hub sub-topics for example the related search data can help come up with ideas that Google already knows is related. The search volume data can also come in handy to identify trending topics based on previous data.
- Match seo content length and quality to the difficulty assessment of the keyword. A 1000 word article may rank well for a low competition keyword whereas a high difficulty keyword may need an entire content hub created and additional link building and outreach.
High Click Through Rate Titles
The percentage of people that click through to your article relative to the ranking position in the search engine results is important. If Google’s algorithm sees that more people are clicking on your page in 4th position than normal it will start to move up the search engine results.
There are three factors to a standard search engine result that affects click through rate. In order of importance they are:-
- Title – Displayed in large blue text and often the only thing seen as a user scans the results.
- URL – An authoritative or recognised domain name get’s higher click through rate. URL directory and filenames are broken down to a simplified breadcrumb navigational structure.
- Description – 160 characters to sell your article and earn the click. This is set in the meta description tag.
The title is by far the most important factor of the three that will affect the click through rate and ultimate success in the SERP’s.
Emojis can be used in titles and descriptions and get passed through to the SERP’s. It’s common to see these used excessively for highly competitive terms. When used well, Emojis can add a visual impact to the search engine listing 👍
How To Write Better Titles
- Write for the visitor! Include words like You and Your.
- Use proven headlines:
- Curated List “7 Simple Tricks To *”
- How To “How To *”
- Searchable Questions “Why does x?”
- Numbers generate clicks
- Emotional words push buttons “Confessions of a x”
- 50-60 characters works best
- Generate enough ambiguity to arouse interest
Title Suggestion Tool
Find this tool useful? Share it on social media
SEO Content Structure
Written SEO content should follow standard HTML markup:-
H1 – Title
H2 – Heading
H3 – Sub-heading
…etc
SEO Content should be well organised and easy to navigate for desktop and mobile users.
For long-form articles include a contents menu to make it easier to navigate between sections of the page.
The contents can act as a starting point for an article and provide the skeleton before individual sections are filled out.
![]()
Amazon’s “look inside” feature lets you view a book’s contents page which can help with inspiration for headings.
Include a “hook and promise” early on in the SEO content. The title will earn the click but the hook should earn the read. Tell readers what they will get out of the article, what is in it for them?
The introduction section should build rapport with the user, build trust, promise a solution to the query.
Include structured content such as tables, bullet points and numbered lists wherever possible.
Most visitors wont read every word on the page so make the SEO content skimable. Can you take away value in 30 seconds from skim reading the content?
Snippet Optimization
Google has rolled out snippets on a vast number of search queries. These are short excerpts that are taken from the website and displayed directly in the Google search results.
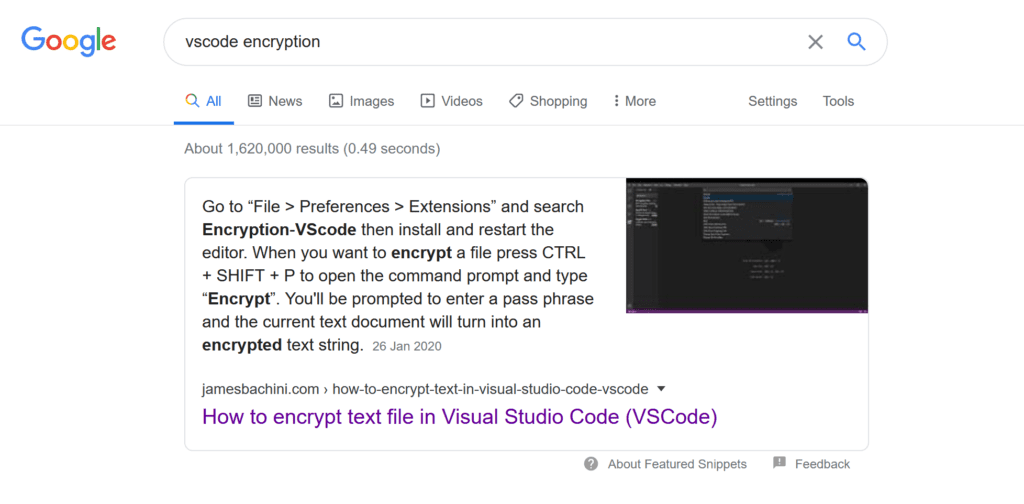
A featured snippet can either be a paragraph, table or list.
- Paragraph – 40-97 word (3-8 lines at 11px)
- List – 4 to 8 bullet points
- Table – 2-3 columns 2-9 rows
Notice in the example above the paragraph has been used alongside an embedded image from the post.
A recent analysis I carried out showed most snippets are taken from the first part of long-form blog posts so it’s a good idea to target this early on in the first 500 words.
How to tee up a featured snippet

Just like this; create a sub-heading for the exact search term and then add the exact content you want to get into the featured snippet. The sub-heading makes it easy for Google’s algorithms to highlight the content it requires.
A featured snippet should be informational rather than opinionated. Google wants to show content from authoritative sources that reads like a dictionary. Give the algorithm what it wants and it can jump your page to the top of the SERP’s.
OnPage Optimization
Here is a checklist to make sure the onPage SEO is as good as possible.
- Keywords should be at start of title
- Title should be optimized for high click through rate
- Keywords should be in description
- Keywords should be hyphenated in the URL
- Hook and promise introduction, what is in it for the reader
- Keywords should appear somewhere in the opening three paragraphs.
- Include keyword in at least one image alt attribute
- Check keyword density and semantic term density, increase where possible
- Target featured snippet in first 500 words
- Include internal and authoritative external links
- Check word count matches keyword difficulty
- Short paragraphs, easy to read as 2nd language
- Optimized fast loading images
- Visually appealing content, colours and layout
- Authoritative – would a manual reviewer consider this a 10/10 authoritative resource?
- Include link bait such as online tools, infographics, original research
- Use table of contents to navigate internally on page
- Include structured content such as tables and lists
Copywriting & Editing
Check Google analytics for any site and go to “Audience > Geo > Language” and check out how many readers are attempting to consume your content in their second language.
Make the content simple and easy to read for everyone. Short words, short sentences, short paragraphs.

Tell stories where possible. Human brains are wired to love storytelling. It’s an artform in itself but read up on the basics and incorporate storytelling in the content.
Be authentic, honest and trustworthy. Talk about failures and successes. Build rapport through open vulnerability and self-confidence.
Know your audience and write for the ideal customer.
Be specific and avoid vague opinions. Google’s algorithm rewards authoritative content.
Write for the reader not for yourself. The first 8 years of this blog I used it as a way to vent and share what I wanted to say, not what readers wanted to hear. Always be adding value.
Spend a lot of time on headlines or that’ll be all the majority of people ever read.
Make the content visually appealing. Magazines tend to do this really well and can provide inspiration for online content. Blogs that are particularly good should be bookmarked and used as a reference.
Edit aggressively. Anything that doesn’t add value should go. How many actionable takeaways are there per section?
Link Building, Outreach & Seed Marketing
Relying on a “build it and they will come” philosophy is less than optimal. Content creators should channel some effort into promoting content to get it out there.
There are three ways in which to do this:-
Link Building
Links from 3rd party sites act as votes and help move content up the search engine rankings.
Link quality is more important than link quantity and a single link from an authoritative news site will hold more weight than a 10000 links purchased off blackhatworld.

Guest blogging is one way to build links and works well for getting some initial links and content in front of an audience. Google “niche guest post guidelines” or “niche write for us” and see what comes up. Also look at the top sites in the industry and see if they have multiple authors. If so reach out with an article and see if it’s suitable for their publication.
Competitor link analysis is the process of analysing competitors link profiles and seeing which ones can be replicated. If a competitor lists in a directory for example it may be possible to get the same link as the directory will have multiple outgoing links for each category.
Paid press releases paid links are officially frowned upon by Google but paid press releases are a good way to get the highest quality backlinks. Contact the editor or advertising department of big sites and ask for advertising rates for press releases. This is how many companies and sites get “featured on Forbes”.
Outreach
Outreach is about naturally connecting on a human level with other industry players. Here’s an example cold email:-
Hi X,
I am collecting industry leader insights to go into an article related to your work at X. Would it be OK to use this quote?
“X”
I’ll link back to https://x.com and I plan on promoting the post with paid ads so that there is some referral traffic too.
If you have no objection could you just reply with OK or another quote you’d prefer I use.
Draft Post: https://googledocs
Blog: https://jamesbachini.com
Kind regards,
James
It’s personalised, short enough they might read it, includes some ego bait which might get a reply and there’s a simplified call to action.
This gets followed up with a “Post is now live: https://jamesbachini.com thank you” which will get shared on the industry leaders social media more times than not.
This is just one example and I wouldn’t copy it word for word. Just reach out, be normal, not spammy and try to add some value for the people you are connecting with.
High achievers and industry leaders who are actively doing business:
- Check and respond to their own email
- Are very curious about new things
- Have little time and energy to spare
Short, attention grabbing, value-add cold emails work well.
Podcast interviews are another way to make real industry connections and most will include a link to a site in the show notes.
Seed Marketing
Once great content has been created it’s a waiting game for Google to decide if it’s worthy of any traffic. This can take between 6-12 months on average. The average top ranked article for competitive terms is 3 years old.
We can wait or be productive and throw some paid advertising at it. There are some huge benefits to this:-
- Naturally builds backlinks and social signals from real users
- Develop an audience quickly, great content = repeat visitors
- Discover related search terms and volumes from broad keyword bidding
- Get exact click through rate metrics and split test titles and descriptions in ads
- Calculate accurately how much search traffic there is for a query
- Get conversion rate metrics to see the real value and buyer intent for the keyword
- Heat maps can show where users are dropping off in the content before Google starts sending traffic
- Get initial feedback from visitors via surveys or feedback buttons
The obvious place to start is Google Ads and just promote using the targeted keywords in Google search.
Facebook and other social media sites are also options to develop a seed audience for the content.
Seed marketing enables a site to gain momentum faster while also delivering valuable data which can help optimize the content for SEO.
7 SEO Content Tips
- Start with keyword research and find a search query that gets traffic but isn’t impossible to rank for.
- Choose a content structure such as long form article, lengthy list, original research, how to guide, content hub, perpetual annual review or video content which fits the keyword difficulty and search intent.
- Create a compelling title which will get more clicks than anything else in the SERP’s. Ensure the target keyword phrase is at the front of the title.
- Create an article structure in the form of a contents page. This can be adjusted later but will act as the skeleton of the content and breakdown the writing into sections.
- Write an introduction with a hook and a promise to build rapport and trust with the reader while promising a solution to the search query.
- Write for the ideal customer and add as much value as possible. Ensure the content is the best and most definitive resource in the SERP’s. It should deserve to rank at the top of the results.
- Use the onpage optimization checklist to ensure the post is optimized to exceed search engine requirements.

This article is part of a free online course where you can learn digital marketing.
If you’ve enjoyed these resources could you help share this content on social media and send it to anyone who you think might benefit from it.
Thank you.



