Decentralised finance is revolutionising the blockchain sector. It provides a playground of opportunities for investors, traders and developers. This article provides a comprehensive in depth guide to everything DeFi.
- What Is Decentralised Finance?
- Applications For Decentralised Finance
- Leading Decentralised Finance Platforms
- Ethereum Congestion and Eth2.0 Staking
- DeFi Yield Farming Example [Video]
- Decentralised Finance Opportunity & Risk
- Developing DeFi Applications
- The Future Of Decentralised Finance
What Is Decentralised Finance?
Decentralised finance is an extension of cryptocurrency and blockchain applications enabling borrowing, lending, trading and investing.
DeFi provides financial services through the use of smart contracts which are executed on a decentralised blockchain. This means that control over the DeFi protocol is distributed to stakeholders rather than controlled by a single entity like a bank.
Applications For Decentralised Finance
Decentralised Borrowing
Decentralised finance took off in the DeFi summer of 2020 when borrowing and lending platforms started offering native tokens as an incentive to use their network.
Borrowing works by depositing cryptocurrency to a smartcontract to be used as collateral and then borrowing a limited amount of funds based on that collateral.
So for example a user might own 10 ETH (Ethereum) which he doesn’t want to sell because he thinks it will go up in value but he needs to pay rent this month. That user can send the ETH to a smart contract which will store it securely until redemption. Then take out a loan (often in stablecoins such as DAI or USDT which is pegged to the USD). So if 1 ETH = $1000 USD then they can normally borrow up to half the value of the collateral. 10 ETH would enable them to borrow $5000 USD which could then be cashed out on an exchange.
If the value of their collateral drops below a set point they will get a margin call and will need to wither add more collateral, pay back the loan or risk liquidation.
In practice this mechanism is often used for trading to take up leveraged positions. The $5000 will eventually need to be paid back with interest to close the loan.
Decentralised Lending
The other side of this is decentralised lending. Most US bank accounts are offering less than 0.1% APR interest rates. DeFi users can convert their cash in to stablecoins such as DAI and USDT which are pegged to the value of the US dollar. Then these can be lent out to borrowers to earn an interest, usually between 3-15%, on those funds.
People that are holding cryptocurrency can also earn an interest on their holdings. This can either be through DeFi lending platforms or via systems such as staking which we will get in to later.
Decentralised lending comes with it’s own risks. There have been instances where entire pools with tens of millions of dollars in collateral have disappeared in what’s known as flash loan attacks.
DeFi Trading and Automated Market Makers AMM
Traditionally users have traded one cryptocurrency for another on a centralised cryptocurrency exchange such as Binance or FTX. The advent of AMM’s such as Uniswap have provided an elegant simplicity to decentralised trading.
A liquidity provider (LP) will provide two assets in equal quantities. So lets assume they provide the following assets from the previous example.
- 1000 USDT
- 1 ETH
They will then get 2000 USD worth of LP tokens and the ETH & USDT will be added to the liquidity pools.
If a trader then comes by and wants to swap ETH for USDT they can exchange tokens adding and subtracting from that pool. So let’s say they provide 100 USDT and want in return 0.1 ETH.
The asset volumes in the liquidity pool will then have shifted so that it contains:
- 1100 USDT
- 0.9 ETH
The valuation of the assets will have shifted so if someone else wants to purchase ETH they will have to pay a higher price. This variation in asset price ends up getting arbitraged away by trading bots if it derives too far from centralised exchange pricing.
The trader pays a fee for this service and the liquidity provider earns a percentage of those fees.
Synthetic Assets
Synthetic assets are a form of derivative product in decentralised finance. Synths are created which follow the price of an underlying asset. For example sTSLA will follow the stock price of Tesla.

Synths are minted via a platform such as Synthetix or Mirror Protocol. Liquidity providers contribute to a underlying asset pool in return for fees and native tokens.
When a trader purchases a synth they are effectively trading against the underlying asset pool as any gains will be taken from it.
Decentralised Insurance
Projects such as Nexus Mutual are building insurance protocols on DeFi smart contracts.
Funds are provided and stored inside the contract which acts as a shared risk pool. Currently the space is targeted towards the risk of capital loss through things like flash loan attacks. In the event of a loss of funds the pool pays out to users who took out insurance.
In the future this seems like an obvious opportunity for growth into other areas such as car, home and life insurance which would rely on some form of oracle to verify claims.
Leading Decentralised Finance Platforms
Here are some of the leading DeFi platforms, what they offer and why they are important.
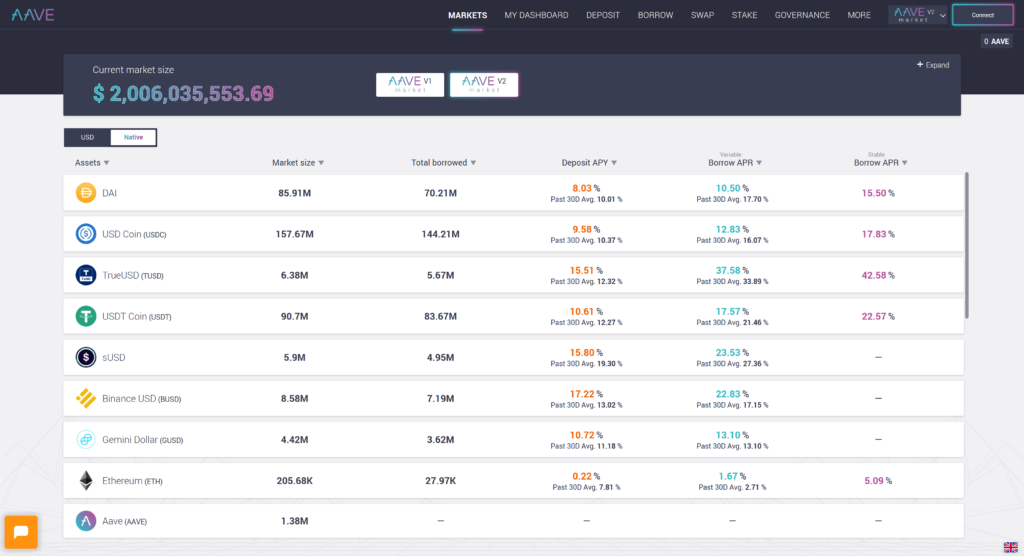
Maker, AAVE & Compound
These are the top three lending and borrowing platforms in DeFi. They have total locked value of around $5,000,000,000 each at time of writing.
Interest rates vary on an hourly basis so money flows in and out depending on who is offering the best rate on a specific asset at that time.
All are built on Ethereum so transaction fees are high at present.
Out of the three I would recommend Aave but check DeFiRate to see what is currently being offered.
Uniswap, SushiSwap & PancakeSwap
Uniswap is the number one AMM and is the most widely used by retail traders looking to swap tokens. It’s simple to connect to a web wallet such as Metamask and exchange tokens at will.
Sushiswap is a competitor which had a controversial start but has now settled into an established place in the market. PancakeSwap is the equivalent AMM for the Binance Smart Chain. This is an alternative to Ethereum with lower transaction fees.
It’s also worth noting that there are platforms such as 1Inch Exchange that routes transactions through the cheapest network.
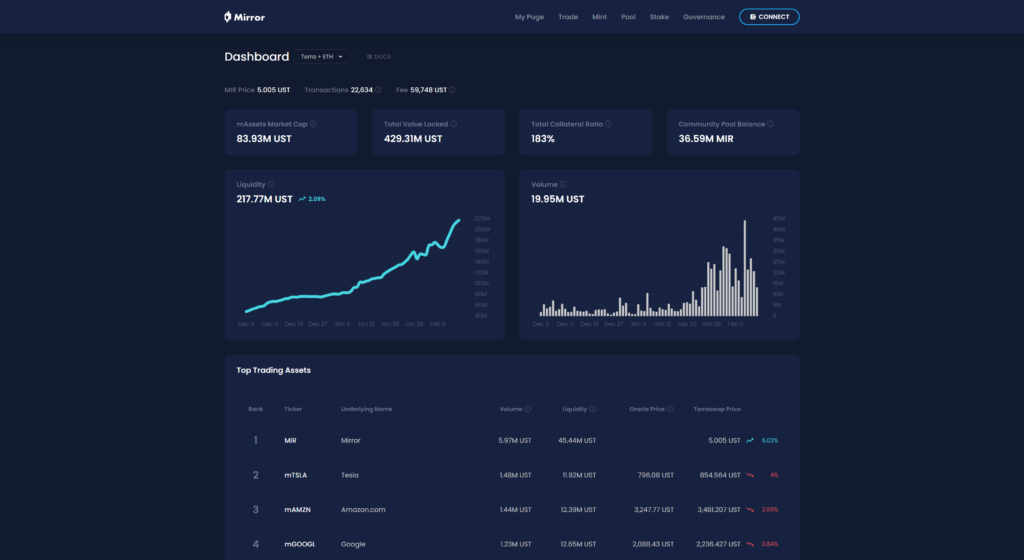
Synthetix, Mirror & BonFida
These are more like traditional exchanges but using a DeFi backend.
Synthetix is the market leader but ethereum network fees have made it almost unusable except for high value transactions.
Mirror protocol is a newer synthetic exchange that is built on the Terra protocol. It’s probably the only place I’d recommend for DeFi trading outside of AMM’s currently.
BonFida is developed on top of Serum by the FTX/Alameda team. It’s built around the Solana protocol and could become a big player in the future.
I’m going to be partaking in the Solana/Serum Hackathon starting on this week to learn more about this ecosystem.
Yearn Finance & AutoFarm
Yearn Finance is a DeFi yield farming platform by renowned developer Andre Cronje. The system works with automated vaults which are designed to automate the process of finding the best yields for an investor.
AutoFarm is the Binance Smart Chain equivalent of YFI which provides high APR vaults and lower fees at present.
AutoFarm can be used to get a yield on liquidity provider tokens from PancakeSwap. Essentially this means providing liquidity in the form of wBNB and AUTO tokens then using the LP tokens to yield farm in AutoFarm.
Ethereum Congestion and Eth2.0 Staking
Everything DeFi was originally built on Ethereum. However as the popularity exploded so did transaction fees and it can now cost over $100 to execute some of the more complex transactions required for decentralised finance.
This has allowed for the emergence of alternative blockchains such as Binance Smart Chain, Terra and Solana. These all provide faster transactions and lower fees than Ethereum can currently offer.
Eth2.0 will fix this. I first started doing development work on blockchain applications in early 2017 and Eth2.0 was already being discussed then. It’s been a long time in the making and the rollout is proving equally slow.
However once rolled out it will revolutionise the industry and disrupt the wider financial sector. Eth2.0 will provide the following updates:-
- Staking via a proof of stake PoS consensus mechanism
- Faster transactions and more capacity via sharding
- Lower transaction costs and less network congestion
This is going to be a pivotal moment for DeFi because it’ll open up huge opportunities for DeFi applications.
Staking is really interesting and worth it’s own blog post but basically if you own ETH you can earn a percentage reward for holding that asset. This is going to appeal and “make sense” to traditional finance institutions because it becomes a revenue generating asset that they can model and value accordingly.
Currently all focus from the media and corporations is on Bitcoin but I believe this will change once Ethereum migrates to a proof of stake network.

Vitalik Buterin the creator of Ethereum described the roll out as creating the foundation on which the future of finance will be built.
I think he’s right and Ethereum really does have the potential not just to disrupt the blockchain sector but revolutionise the entire financial industry over the next few decades.
DeFi Yield Farming Example [Video]
This video shows the process of providing liquidity to an AMM and then using the LP tokens to yield farm on the Binance Smart Chain, all with a $20 budget.

Decentralised Finance Opportunity & Risk
For investors decentralised finance offers exciting returns but it also involves a difficult to quantify amount of risk. Let’s looks at some of these risks individually.
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Contract Bugs | Code deployed in smart contracts can’t be altered. It’s not like a normal application that gets updates. When something needs changing the developers need to roll out new contracts and then move everyone across. This also means that bugs are critical and extremely dangerous because it can lock funds in a contract which aren’t able to be retrieved. Generally speaking the more widely used a smart contract is the less likely it is to contain a critical bug as it will have been probed for bugs by auditors and hackers already. |
| Collapse of Asset Value | A token is a form of collectible and only holds value if someone else agrees on that value. There’s been a lot of talk about the risks associated with centralised stablecoins such as USDT and their operators. If the value of an asset goes to zero then it’s irrelevant how much return that asset can provide. |
| Hacks & Flash Loan Attacks | There is a significant chance of loss of funds through hacks in the DeFi space. In 2020 hundreds of millions were lost to flash loan attacks. Code auditing helps to prevent catastrophes but doesn’t guarantee the safety of a protocol. |
| Rug Pulls | This is where the creator of a DeFi protocol basically does a runner with everyones money. Sushiswap famously went through this and came out the other side when the founder returned the funds. The newer a protocol the larger the opportunity for oversized returns but also the higher the risk. Careful due diligence and sensible investing is key. |
| Lost Keys | DeFi has the same risks associated with managing personal cryptocurrency holdings. You are responsible for your own keys and wallets. These for the most part can’t be recovered and there is no central support desk to help. |
This may read like a horror story but it’s important to understand these risks. To put them in perspective some products provide less than 3% yield per year and people smarter than me are willing to risk their assets for that return.
The more established a DeFi protocol is and the more money it has locked up the less risk there is associated with using it in my opinion.
I wouldn’t think twice about using Uniswap for example because I know that there’s billions of dollars at stake and the code has been audited and used by the best developers in the industry.
Developing DeFi Applications
While the obvious opportunity for decentralised finance is for investors and traders there is still a lot of room for further development.
DeFi development is mainly focused on smart contracts and both Ethereum and the interoperable Binance Smart Chain is Solidity.
Developing smart contracts is different from normal web or application based development work. It’s a slower process where every line must be mulled over and debated. There is literally zero room for errors and bugs.
Where possible it’s a good idea to use existing code in the form of modules, functions and templates provided by existing DeFi protocols. This is described as lego money where existing code can be used like lego bricks to complete specific functions within a smart contract. The less code you write the safer it is, in theory.
There’s a useful primer with more information from Instadapp: https://docs.instadapp.io/
Check out the Solidity playground for a web based IDE: https://remix.ethereum.org/
The Future Of Decentralised Finance

There is a missing piece currently to the DeFi space which is oracles. While projects like Chainlink and Dia can provide price updates to a blockchain it’s still not possible to do something like an online credit rating check.
This is likely to change in the next few years and DeFi will start to expand in to traditional financial markets. There has already been cases of people funding house purchases using DeFi but we will see a lot more of this once oracles become more commonplace.
In essence liquidity providers could contribute to a pool of funds which could be used to provide mortgages, insurance, personal loans and anything else that is currently provided by your high street bank.
The protocols will only be as effective as the data and management provided by the oracle and this will likely prove to become a competitive landscape.
Ethereum 2.0 which is expected to be deployed in a number of stages throughout 2021 and 2022 will expand the capacity of the underlying network and open up things like staking which will attract interest from the largest financial institutions.
Should you be involved in DeFi? I’d suggest that it’s worth at least trying out. You can set up an account with Binance and move $20 of funds around on the Binance Smart Chain to see what it’s all about and get a feel for the disruption that is taking place in decentralised finance.


